PHP Laravel 7/6 Tutorial: CRUD Example App with Bootstrap 4 and MySQL Database
Throughout this tutorial for beginners you'll learn to use Laravel 7/6 - the latest version of one of the most popular PHP frameworks - to create a CRUD web application with a MySQL database and Bootstrap 4 styles from scratch and step by step starting with the installation of Composer (PHP package manager) to implementing and serving your application.
Note: Laravel 7 is recently released and this tutorial is upgraded to the latest version.
Also check out PHP Laravel 7 Tutorial By Example: Build Your CRUD App With MySQL And CSS Bootstrap
Latest from laravel
Bookmark This Article
Your browser doesn't support automatic bookmarking. You can:
- Press Ctrl+D (or Command+D on Mac) to bookmark this page
- Or drag this link to your bookmarks bar:
Clicking this bookmarklet when on any page of our site will bookmark the current page.
What is Bootstrap 4?
Bootstrap 4 is the latest version of Twitter Bootstrap which is a CSS framework that allows web developers to professionally style their web interfaces without being experts in CSS.
Bootstrap 4 is based on Flexbox and allows you to build responsive layouts with easy classes and utilities.
Also read How to Install Bootstrap 4 in Laravel 7/6 Tutorial and Example
What is CRUD?
CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update and Delete which are operations needed in most data-driven apps that access and work with data from a database.
In this example, we'll see how to impelement the CRUD operations in Laravel 7/6 against a MySQL database.
Also read: Laravel 7/6 REST CRUD API - Eloquent Models and Relationships
Laravel 7 New Features
Laravel 7 brings many new features such as:
- Laravel Airlock: An official package for API authentication,
- Custom Eloquent Casts: They allow you add your won custom casts,
- CORS support by default i.e without third-party plugins,
- Blade Component Tags & Improvements: Allows you to create class-less components,
- HTTP Client: An API for making HTTP requests,
- Route Caching Speed Improvements, etc.
Also read Laravel 7/6 Auth Tutorial: Login/Register/Password Reset Example
The New Features of Laravel 6
So, what is new with Laravel 6?
As mentionned, Laravel 6 comes with a bunch of new features and enhancements such as:
- The support of Semantic Versioning,
- Compatibility with Vapor, a serverless deployment platform for Laravel,
- Improved Authorization Responses,
- Job Middleware: A new feature that allows you wrap custom logic around the execution of queued jobs,
- Lazy Collections: A new feature that leverages PHP's generators to enable you to efficently work with very large datasets,
- Eloquent Subquery Enhancements,
- Laravel UI: UI scaffolding logic such as Bootstrap or Vue, is extracted in its own
laravel/uipackage. - Ignition: A new and smart error page.
Check out the docs for more details.
Laravel 5.8 New Features
Let's start our tutorial by going through the most important features introduced in this version.
- The
hasOneThroughEloquent relationship. - Better email validation,
- Auto-Discovery Of Model Policies provided that the model and policy follow standard Laravel naming conventions
- DynamoDB cache and session drivers,
- Added support for PHPUnit 8.0 for unit testing,
- Added support for Carbon 2.0, an easy to use PHP API extension for DateTime,
- Added support Pheanstalk 4.0: a pure PHP 5.3+ client for the beanstalkd workqueue, etc.
The Laravel 6 version has also corrected numeroous bugs and introduced many improvements of the Artisan CLI.
Check out the official docs for details features of Laravel 5.8
Prerequisites
This tutorial assumes you have PHP and MySQL installed on your system. Follow the instructions for your operating system to install both of them.
You also need to be familiar with Linux/macOS bash where we'll be executing the commands in this tutorial.
Familiarly with PHP is required since Laravel 7 is based on PHP.
For development I will be using a Ubuntu 16.04+ machine so the commands in this tutorial are targeting this system but you should be able to follow this tutorial in any operating system you use.
Laravel 6 requires PHP >= 7.2.0 Laravel 7 requires PHP >= 7.2.5
Installing PHP 7.2.5+
Laravel 7 requires PHP 7.2.5+ or above so you need the latest version of PHP installed on your system. The process is straightforward on most systems.
On Ubuntu, you can follow these instructions.
First add the ondrej/php PPA which contains the latest version of PHP:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php
$ sudo apt-get update
Next, install PHP 7.2 using the following command:
$ sudo apt-get install php7.2
If you are using Ubuntu 18.04, PHP 7.2 is included in the default Ubuntu repository for 18.04 so you should be able to install it using the following command:
$ sudo apt-get install php
This tutorial is tested with PHP 7.2 but you can also use more recent versions like PHP 7.3
Installing the Required PHP 7.2 Modules
Laravel requires a bunch of modules. You can install them using the following command:
$ sudo apt-get install php7.2 php7.2-cli php7.2-common php7.2-json php7.2-opcache php7.2-mysql php7.2-mbstring php7.2-mcrypt php7.2-zip php7.2-fpm php7.2-xml
Installing PHP Composer
Let's start our journey by install Composer, The PHP package manager.
Navigate in your home directory, then download the installer from the official website using curl:
$ cd ~
$ curl -sS https://getcomposer.org/installer -o composer-setup.php
You can then install composer globally on your system by using the following command:
$ sudo php composer-setup.php --install-dir=/usr/local/bin --filename=composer
As of this writing Composer 1.8 will be installed on your system. You can make sure your installation works as expected by running composer in your terminal:
$ composer
You should get the following output:
______
/ ____/___ ____ ___ ____ ____ ________ _____
/ / / __ \/ __ `__ \/ __ \/ __ \/ ___/ _ \/ ___/
/ /___/ /_/ / / / / / / /_/ / /_/ (__ ) __/ /
\____/\____/_/ /_/ /_/ .___/\____/____/\___/_/
/_/
Composer version 1.8.0 2018-12-03 10:31:16
Usage:
command [options] [arguments]
Options:
-h, --help Display this help message
-q, --quiet Do not output any message
-V, --version Display this application version
--ansi Force ANSI output
--no-ansi Disable ANSI output
-n, --no-interaction Do not ask any interactive question
--profile Display timing and memory usage information
--no-plugins Whether to disable plugins.
-d, --working-dir=WORKING-DIR If specified, use the given directory as working directory.
-v|vv|vvv, --verbose Increase the verbosity of messages: 1 for normal output, 2 for more verbose output and 3 for debug
For more information check out this tutorial.
If you've successfully installed Composer in your system, you are ready to create a Laravel 7 project.
Installing and Creating a Laravel 7 Project
In this section we'll introduce Laravel and then proceed it to install and create a Laravel 7 project.
About Laravel
Laravel docs describe it as:
Laravel is a web application framework with expressive, elegant syntax. We believe development must be an enjoyable and creative experience to be truly fulfilling. Laravel attempts to take the pain out of development by easing common tasks used in the majority of web projects, such as:
- Simple, fast routing engine.
- Powerful dependency injection container.
- Multiple back-ends for session and cache storage.
- Expressive, intuitive database ORM.
- Database agnostic schema migrations.
- Robust background job processing.
- Real-time event broadcasting.
Laravel is accessible, yet powerful, providing tools needed for large, robust applications.
Generating a Laravel 7 project is easy and straightforward. In your terminal, run the following command:
$ composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel laravel-7-crud-app
This will install laravel/laravel v7.
Note: Make sure you have PHP 7.2.5+ installed on your system. Otherwise, composer will use a previous version of Laravel for your project.
You can verify the installed version in your project using:
$ cd laravel-7-crud-app
$ php artisan -V
Laravel Framework 7
Installing the Front-End Dependencies
In your generated project, you can see that a package.json file is generated which includes many front-end libraries that can be used by your project:
- axios,
- bootstrap,
- cross-env,
- jquery,
- laravel-mix,
- lodash,
- popper.js,
- resolve-url-loader,
- sass,
- sass-loader,
- vue.
Note: You can use your preferred libraries with Laravel not specifically the ones added to
package.json.The
package.jsonfile in your Laravel project includes a few packages such asvueandaxiosto help you get started building your JavaScript application.It also includes
bootstrapto help you get started with Bootstrap for styling your UI.It include Laravel Mix to help you compile your SASS files to plain CSS.
You need to use npm to install the front-end dependencies:
$ npm install
After running this command a node_modules folder will be created and the dependencies will be installed into it.
Note: You need to have Node.js and npm installed on your system before you can install the front-end dependencies.
Creating a MySQL Database
Let's now create a MySQL database that we'll use to persist dat ain our Laravel application. In your terminal, run the following command to run the mysql client:
$ mysql -u root -p
When prompted, enter the password for your MySQL server when you've installed it.
Next, run the following SQL statement to create a db database:
mysql> create database db;
Open the .env file and update the credentials to access your MySQL database:
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=127.0.0.1
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=db
DB_USERNAME=root
DB_PASSWORD=******
You need to enter the database name, the username and password.
At this point, you can run the migrate command to create your database and a bunch of SQL tables needed by Laravel:
$ php artisan migrate
Note: You can run the
migratecommand at any other points of your development to add other SQL tables in your database or to later your database if you need to add any changes later.
Creating your First Laravel Model
Laravel uses the MVC architectural pattern to organize your application in three decoupled parts:
- The Model which encapsulates the data access layer,
- The View which encapsulates the representation layer,
- Controller which encapsulates the code to control the application and communicates with the model and view layers.
Wikipedia defines MVC as:
Model–view–controller is an architectural pattern commonly used for developing user interfacesthat divides an application into three interconnected parts. This is done to separate internal representations of information from the ways information is presented to and accepted from the user.
See Laravel 7/6 Database Migrations Tutorial with Admin Roles Example
Now, let's create our first Laravel Model. In your terminal, run the following command:
$ php artisan make:model Contact --migration
This will create a Contact model and a migration file. In the terminal, we get an output similar to:
Model created successfully.
Created Migration: 2019_01_27_193840_create_contacts_table
Open the database/migrations/xxxxxx_create_contacts_table migration file and update it accordingly:
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreateContactsTable extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('contacts', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->timestamps();
$table->string('first_name');
$table->string('last_name');
$table->string('email');
$table->string('job_title');
$table->string('city');
$table->string('country');
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('contacts');
}
}
We added the first_name, last_name, email, job_title, city and country fields in the contacts table.
Also see, Laravel 7/6 Email Verification Tutorial and Example
You can now create the contacts table in the database using the following command:
$ php artisan migrate
Now, let's look at our Contact model, which will be used to interact with the contacts database table. Open the app/Contact.php and update it:
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Contact extends Model
{
protected $fillable = [
'first_name',
'last_name',
'email',
'city',
'country',
'job_title'
];
}
Creating the Controller and Routes
After creating the model and migrated our database. Let's now create the controller and the routes for working with the Contact model. In your terminal, run the following command:
$ php artisan make:controller ContactController --resource
Laravel resource routing assigns the typical "CRUD" routes to a controller with a single line of code. For example, you may wish to create a controller that handles all HTTP requests for "photos" stored by your application. Using the
make:controllerArtisan command, we can quickly create such a controller:This command will generate a controller at
app/Http/Controllers/PhotoController.php. The controller will contain a method for each of the available resource operations.
Open the app/Http/Controllers/ContactController.php file. This is the initial content:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class ContactController extends Controller
{
/**
* Display a listing of the resource.
*
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function index()
{
//
}
/**
* Show the form for creating a new resource.
*
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function create()
{
//
}
/**
* Store a newly created resource in storage.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function store(Request $request)
{
//
}
/**
* Display the specified resource.
*
* @param int $id
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function show($id)
{
//
}
/**
* Show the form for editing the specified resource.
*
* @param int $id
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function edit($id)
{
//
}
/**
* Update the specified resource in storage.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @param int $id
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function update(Request $request, $id)
{
//
}
/**
* Remove the specified resource from storage.
*
* @param int $id
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function destroy($id)
{
//
}
}
The ContactController class extends Controller class available from Laravel and defines a bunch of methods which will be used to do the CRUD operations against the Contact model.
You can read the role of the method on the comment above it.
Now we need to provide implementations for these methods.
But before that, let's add routing. Open the routes/web.php file and update it accordingly:
<?php
Route::get('/', function () {
return view('welcome');
});
Route::resource('contacts', 'ContactController');
Using the resource() static method of Route, you can create multiple routes to expose multiple actions on the resource.
These routes are mapped to various ContactController methods which will need to implement in the next section:
- GET
/contacts, mapped to theindex()method, - GET
/contacts/create, mapped to thecreate()method, - POST
/contacts, mapped to thestore()method, - GET
/contacts/{contact}, mapped to theshow()method, - GET
/contacts/{contact}/edit, mapped to theedit()method, - PUT/PATCH
/contacts/{contact}, mapped to theupdate()method, - DELETE
/contacts/{contact}, mapped to thedestroy()method.
These routes are used to serve HTML templates and also as API endpoints for working with the Contact model.
Note: If you want to create a controller that will only expose a RESTful API, you can use the
apiResourcemethod to exclude the routes that are used to serve the HTML templates:
Route::apiResource('contacts', 'ContactController');
Implementing the CRUD Operations
Let's now implement the controller methods alongside the views.
C: Implementing the Create Operation and Adding a Form
The ContactController includes the store() method that maps to the POST /contacts API endpoint which will be used to create a contact in the database and the create() that maps to the GET /contacts/create route which will be used to serve the HTML form used to submit the contact to POST /contacts API endpoint.
Let's implement these two methods.
Re-open the app/Http/Controllers/ContactController.php file and start by importing the Contact model:
use App\Contact;
Next, locate the store() method and update it accordingly:
public function store(Request $request)
{
$request->validate([
'first_name'=>'required',
'last_name'=>'required',
'email'=>'required'
]);
$contact = new Contact([
'first_name' => $request->get('first_name'),
'last_name' => $request->get('last_name'),
'email' => $request->get('email'),
'job_title' => $request->get('job_title'),
'city' => $request->get('city'),
'country' => $request->get('country')
]);
$contact->save();
return redirect('/contacts')->with('success', 'Contact saved!');
}
Next, locate the create() method and update it:
public function create()
{
return view('contacts.create');
}
The create() function makes use of the view() method to return the create.blade.php template which needs to be present in the resources/views folder.
Before creating the create.blade.php template we need to create a base template that will be extended by the create template and all the other templates that will create later in this tutorial.
In the resources/views folder, create a base.blade.php file:
$ cd resources/views
$ touch base.blade.php
Open the resources/views/base.blade.php file and add the following blade template:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Laravel 7 & MySQL CRUD Tutorial</title>
<link href="{{ asset('css/app.css') }}" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
@yield('main')
</div>
<script src="{{ asset('js/app.js') }}" type="text/js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Now, let's create the create.blade.php template. First, create a contacts folder in the views folder:
$ mkdir contacts
Next, create the template
$ cd contacts
$ touch create.blade.php
Open the resources/views/contacts/create.blade.php file and add the following code:
@extends('base')
@section('main')
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-8 offset-sm-2">
<h1 class="display-3">Add a contact</h1>
<div>
@if ($errors->any())
<div class="alert alert-danger">
<ul>
@foreach ($errors->all() as $error)
<li>{{ $error }}</li>
@endforeach
</ul>
</div><br />
@endif
<form method="post" action="{{ route('contacts.store') }}">
@csrf
<div class="form-group">
<label for="first_name">First Name:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="first_name"/>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="last_name">Last Name:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="last_name"/>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="email"/>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="city">City:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="city"/>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="country">Country:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="country"/>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="job_title">Job Title:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="job_title"/>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary-outline">Add contact</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
@endsection
This is a screenshot of our create form!
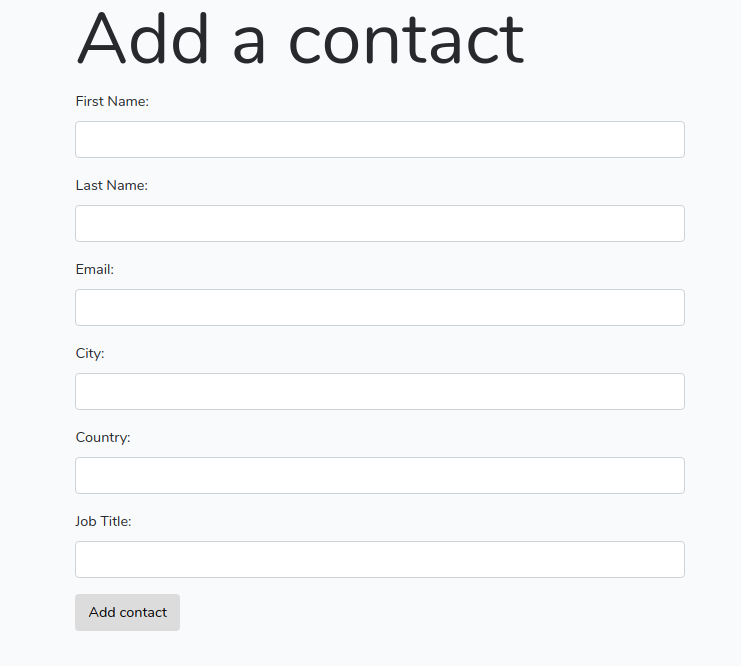
Fill out the form and click on the Add contact button to create a contact in the database. You should be redirected to /contacts route which doesn't have a view associated to it yet.
R: Implementing the Read Operation and Getting Data
Next, let's implement the read operation to get and display contacts data from our MySQL database.
Go to the app/Http/Controllers/ContactController.php file, locate the index() method and update it:
public function index()
{
$contacts = Contact::all();
return view('contacts.index', compact('contacts'));
}
Next, you need to create the the index template. Create a resources/views/contacts.index.blade.php file:
$ touch index.blade.php
Open the resources/views/contacts/index.blade.php file and add the following code:
@extends('base')
@section('main')
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-12">
<h1 class="display-3">Contacts</h1>
<table class="table table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
<td>ID</td>
<td>Name</td>
<td>Email</td>
<td>Job Title</td>
<td>City</td>
<td>Country</td>
<td colspan = 2>Actions</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach($contacts as $contact)
<tr>
<td>{{$contact->id}}</td>
<td>{{$contact->first_name}} {{$contact->last_name}}</td>
<td>{{$contact->email}}</td>
<td>{{$contact->job_title}}</td>
<td>{{$contact->city}}</td>
<td>{{$contact->country}}</td>
<td>
<a href="{{ route('contacts.edit',$contact->id)}}" class="btn btn-primary">Edit</a>
</td>
<td>
<form action="{{ route('contacts.destroy', $contact->id)}}" method="post">
@csrf
@method('DELETE')
<button class="btn btn-danger" type="submit">Delete</button>
</form>
</td>
</tr>
@endforeach
</tbody>
</table>
<div>
</div>
@endsection
U: Implementing the Update Operation
Next, we need to implement the update operation. Go to the app/Http/Controllers/ContactController.php file, locate the edit($id) method and update it:
public function edit($id)
{
$contact = Contact::find($id);
return view('contacts.edit', compact('contact'));
}
Next, you need to implement the update() method:
public function update(Request $request, $id)
{
$request->validate([
'first_name'=>'required',
'last_name'=>'required',
'email'=>'required'
]);
$contact = Contact::find($id);
$contact->first_name = $request->get('first_name');
$contact->last_name = $request->get('last_name');
$contact->email = $request->get('email');
$contact->job_title = $request->get('job_title');
$contact->city = $request->get('city');
$contact->country = $request->get('country');
$contact->save();
return redirect('/contacts')->with('success', 'Contact updated!');
}
Now, you need to add the edit template. Inside the resources/views/contacts/, create an edit.blade.php file:
$ touch edit.blade.php
Open the resources/views/contacts/edit.blade.php file and add this code:
@extends('base')
@section('main')
<div class="row">
<div class="col-sm-8 offset-sm-2">
<h1 class="display-3">Update a contact</h1>
@if ($errors->any())
<div class="alert alert-danger">
<ul>
@foreach ($errors->all() as $error)
<li>{{ $error }}</li>
@endforeach
</ul>
</div>
<br />
@endif
<form method="post" action="{{ route('contacts.update', $contact->id) }}">
@method('PATCH')
@csrf
<div class="form-group">
<label for="first_name">First Name:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="first_name" value={{ $contact->first_name }} />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="last_name">Last Name:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="last_name" value={{ $contact->last_name }} />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="email" value={{ $contact->email }} />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="city">City:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="city" value={{ $contact->city }} />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="country">Country:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="country" value={{ $contact->country }} />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="job_title">Job Title:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="job_title" value={{ $contact->job_title }} />
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Update</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
@endsection
U: Implementing the Delete Operation
Finally, we'll proceed to implement the delete operation. Go to the app/Http/Controllers/ContactController.php file, locate the destroy() method and update it accordingly:
public function destroy($id)
{
$contact = Contact::find($id);
$contact->delete();
return redirect('/contacts')->with('success', 'Contact deleted!');
}
You can notice that when we redirect to the /contacts route in our CRUD API methods, we also pass a success message but it doesn't appear in our index template. Let's change that!
Go to the resources/views/contacts/index.blade.php file and add the following code:
<div class="col-sm-12">
@if(session()->get('success'))
<div class="alert alert-success">
{{ session()->get('success') }}
</div>
@endif
</div>
We also need to add a button to takes us to the create form. Add this code below the header:
<div>
<a style="margin: 19px;" href="{{ route('contacts.create')}}" class="btn btn-primary">New contact</a>
</div>
This is a screenshot of the page after we created a contact:

Conclusion
We've reached the end of this tutorial. We created a CRUD application with Laravel 7/6, PHP 7 and MySQL.
Hope you enjoyed the tutorial and see you in the next one!







